What's in the etc folder? How to open your ETC file
Hello, dear readers of the blog site. Today I want to talk about something quite simple in its design, like Hosts file.
What’s remarkable is that he lives on almost everyone operating systems(and therefore all computers of Internet users), starting from Linux and ending with Windows 7. Another distinctive property of it is that it does not have an extension, but this is due precisely to the fact that it must work in any OS, and therefore must be universal.
But this is not the main thing. Although he is a relic of the past, there are still a lot of ways to use Hosts both for good purposes and not so good. For example, viruses and virus writers love it very much and often use it either to replace official sites with their phishing duplicates, or to block the ability to update your antivirus program.
However network equipment IP specialists are needed and nothing else. Therefore, a list of correspondence between the host name and its IP address () was manually generated. This list was called named Hosts and sent to all nodes local network. Everything was great until the moment when it was no longer possible to use this method due to huge number records contained in this file. Sending it out has become problematic.
In this regard, we decided to approach this issue differently, namely, to place on the Internet an entire (domain name system) that would store all these correspondence tables and user computers would contact the nearest one with the question of what kind of IP-ish corresponds to the Vasya.ru domain.
At the same time, everyone happily forgot about the Hosts file, but it still existed in all operating systems, except that its content was extremely meager. Usually there was and is still present only one entry:
127.0.0.1 localhost
For some reason, this IP address (more precisely the range 127.0.0.1 - 127.255.255.255) was chosen to designate the local host (private IP), i.e. the very computer you are sitting at (literally localhost - “this computer”). But, really, this is all for the old IPv4 (fourth version).
And in IPv6, which is now coming into use (due to the fact that it is embedded in previous version the number of addresses is no longer enough for everyone) such an entry will look a little different:
::1 localhost
But the essence is the same. Because Now both standards for specifying an IP address are still used or can be used, then in the Hosts file Usually both of these lines are present. True, there can be any kind of billboard written above them (depending on the OS used), but all those lines contain at the beginning the hash symbol # (hash), which means that these lines are comments and should not be taken into account.
On my old lady Windows Vista The Hosts file now looks like this:
# Copyright (c) 1993-1999 Microsoft Corp. # # This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows. # # This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each # entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should # be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name. # The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one # space. # # Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual # lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol. # # For example: # # 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server # 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host # This HOSTS file created by Dr.Web Anti-rootkit API 127.0.0.1 localhost:: 1 localhost
Recording syntax very simple - first indicate the IP address, and then, through any number of spaces (tab characters), enter the name of the host (computer, node or domain). A separate line is used for each entry of this kind.
It gets up here main question, and what place does Hosts currently occupy in the process of establishing a correspondence between domain names entered in the browser and those IP addresses that are hidden behind these domains? Well, as it turned out, very much so important place occupies, namely the first. But first things first.
So, you enter Url address () into the address bar of your browser, or follow a link from your browser bookmarks, or from any web page open in it. In any case, the browser receives from you the path to the document you want to see.
In any case, there will be a presence in Urla domain name the site on which the document you are interested in is located (the site in our example). However, this domain corresponds to a very specific server (maybe virtual) where this very site is hosted. And this server must have must be an IP address, so that it is visible on the network and can be accessed.
Your browser cannot know which IP corresponds to the domain name contained in the URL (well, unless you have enabled caching in this very browser DNS records and this node has been previously visited by you). Therefore he addresses first For clarification, refer specifically to the Hosts file on your computer.
If this domain is not found there (and the corresponding IP), then the browser will begin to torture DNS record caching service from Windows. If you previously accessed this domain and not much time has passed since then, then the DNS cache will give the browser this same IP address. The browser will receive it and open the document you requested.
If there are no records for this domain in the cache, then the browser will send a request to the nearest DNS server (most likely, it will be the server of your Internet provider) and receive the required information from it. True, in this case there may be a slight delay in opening the web page you requested, but with modern Internet speeds this will be practically unnoticeable.
And this happens with absolutely any request to open a document from the Internet from your computer. Do you get it? Empty Hosts does not create any problems, but if you fill it out, and even with malicious intent, it may turn out that you enter the password for your Yandex wallet not on the official website of this payment system, and on a phishing resource with a similar design (see).
How can this be? Well, no one is safe from virus infection (), and a virus can easily add the IP address of a phishing resource to Hosts and assign it the domain name money.yandex.ru, for example. This is where the danger lies.
On a fake site social network they may intercept the passwords you enter, they may demand an entrance fee, or something else more creative. The saddest thing is that it is impossible to notice the substitution, because in address bar browser will display the correct domain name.
Where is the Hosts file located and how can I remove virus entries from it?
On the other side remove changes made by the virus even an absolute noob in computers can use the Host file. Usually the problem is to find where this file is located.
In older versions of Windows, such as XP or 2000, it was open to everyone and lived in system folders at the following address:
Windows\System32\drivers\etc\
You won’t believe it, but he lives at the same address in both Windows 7 and Vista, but everything is somewhat more complicated there, because following the path:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\
You won't find the etc folders there. The developers decided that ordinary mortals should not touch this file to avoid problems.
However, hosts file in windows 7 and vista still exists, you just need to look for it, having received Administrator rights. Personally, I never even tried to figure out all this nonsense with rights, but I found a very simple way for myself to get around this limitation.
So, go to the “Start” button menu - “All Programs” and find the “Accessories” folder there. There are shortcuts inside it, among which it’s easy to see “Notepad”. Click on it right click mouse and from the context menu that appears, select "Run as Administrator":
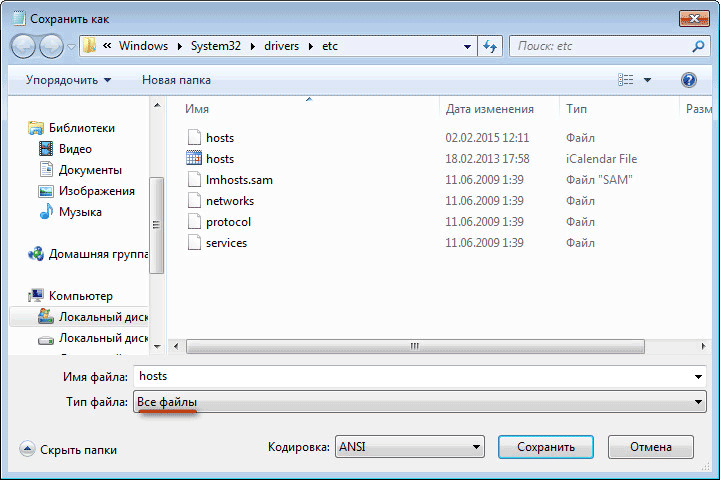
Well, actually, half the battle is done. Now in the notepad you select from top menu items “File” - “Open”. In a standard window Windows Explorer find the desired folder etc (inside the Windows\System32\drivers\ directory), select “All files” from the drop-down list in the lower right corner and watch with happy eyes the appearance of this top-secret file:

It will be exactly without expansion, and the rest will be rubbish, it seems hosts.txt, viruses are very often created to distract your attention and ultimately confuse you. For a real file, they set the “Hidden” attribute, which can be checked or unchecked by simply right-clicking on the file and selecting the very bottom “Properties” item:

And because in Windows, by default, extensions are not displayed for registered file types (that’s why they did this - I don’t understand), then the user finds hosts.txt without seeing either its extension, or the fact that there is another hosts in the same folder, but it is hidden from his eyes.
Making changes to the fake, he still achieves nothing, begins to tear out his hair, wring his hands and goes to the store to buy a new laptop in order to finally get into his favorite Contact, which the virus blocked on the old computer. Ahhh, horror.
Although, of course, the user may be advanced and enable the display of hidden and system files in the settings. In Windows Vista, to do this, go to “Control Panel” - “Folder Options” - “View” tab and move the checkbox to the “Show” hidden folders and files." By the way, it would be better to uncheck the “Hide extensions...” line above:

Eat a very simple way to open this file. It will be enough to press the Win+R key combination on your keyboard (or select “Run” from the “Start” button menu), and then enter in the window that opens next line and press Enter:
Notepad %windir%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts

But that's not the point. We still found where this secret (for Windows 7 and vista) file is located, and we must carefully examine it for possible abuse. If the initial examination of the patient does not reveal any pathologies, then look to the page scroll area in Notepad.
Sometimes the virus makes its entries after several hundred empty lines, thereby reducing the risk of your detection. If there is no scroll bar, then everything is great, but if there is, then use it and bring your Hosts to the form it should have from birth, i.e. It will be enough to have just two lines in it (no one needs comments):
127.0.0.1 localhost::1 localhost
Well, if spoofing addresses in this file it is quite simple to represent, for example it might look like this:
127.0.0.1 localhost::1 localhost 77.88.21.3 site
How, in this case, is it carried out? blocking certain sites through Hosts? Well, just assign the private IP address 127.0.0.1 to the domain that needs to be blocked, for example, like this:
127.0.0.1 localhost::1 localhost 127.0.0.1 vk.com 127.0.0.1 odnoklassniki.ru
The smart browser finds this match and tries to get required document(web page) from your own computer, which, naturally, he cannot do and which he will immediately inform you about. By the way, this good way block your children’s access to sites that you think they should not visit. Of course, you will still need to create a list of such sites or get them from somewhere, but if you wish, you can try.
As I already mentioned, in ancient times, when the Internet was still slow for most users, to speed up the opening of sites, they registered their IP names in Hosts. Another thing is that these same resources periodically changed their hosting and, along with it, their IP addresses. And the user, having forgotten about what he did six months ago to speed up the Internet, tries in vain to understand why his favorite resources are not available to him.
How to use Hosts when moving a website to a new hosting?
Well, and finally, I would like to talk about how, by making changes to the Hosts file, you can work with a site that has moved to new hosting even before everyone DNS servers a new entry will be registered (assigning a new IP address to your domain). The method is very simple but effective.
So, you change hoster. Naturally, the IP address of your site also changes. How will people find out about this on the Internet? Everything is correct, using a network of DNS servers. By the way, the first and most important step You can do it yourself by going to the control panel of your registrar and registering there the addresses of the NS servers of your new hoster.
It is from them that the new DNS will spread throughout the Internet. But this process is lengthy and in the worst case scenario it can take a couple of days. During this time, the site should be available on both the new and old hosting, so that users from all over the world would not be deprived of the opportunity to view it.
However, you yourself will be interested to know how your resource actually feels with the new hoster? Check the operation of all plugins and other things. Do you really have to wait from several hours to two days? After all, this is unbearable.
Firstly, you can try resetting the DNS cache on your own computer, because it may prevent you from seeing your resource on the new hosting if external DNS servers have already received new entry. How to do this? Again, everything is very simple. Press the Win+R key combination on your keyboard (or select “Run” from the Start button menu), then enter in the window that opens:
A very scary window called Command Prompt will open, where you will need to paste this command:
Ipconfig /flushdns
Regular buttons Pasting in the Command Prompt window doesn't work, so just right-click in it and select Paste.

After that, click on “Enter”, the DNS cache will be cleared on your computer and you can try to open your site again. By the way, there may be a DNS cache in the browser itself, so clear it, or refresh the window while holding down the Shift button on the keyboard.
By the way, if you are interested, you can view the contents of the DNS cache by entering command line the following command:
Ipconfig /displaydns
Does the site still open on the old hosting? No problem. We find the Hosts file using the method described just above and add just one line to it:
109.120.169.66 website
Where 109.120.169.66 - it will be IP address of your new hosting, and then the domain name of your site will follow. All. While the rest of the world is admiring your resource on the old hosting, you have the opportunity to correct possible problems on the engine that has already been transferred to the new hosting. The thing is wonderful and I always use it.
Good luck to you! See you soon on the pages of the blog site
You can watch more videos by going to");">

You might be interested
What is DNS and how DNS servers ensure the Internet works VPS from NeoServer - become the owner of your virtual universe  How to make a backup and restore from backup copy, as well as the nuances of transferring a site (Joomla, WordPress) to a new hosting
How to make a backup and restore from backup copy, as well as the nuances of transferring a site (Joomla, WordPress) to a new hosting  Buying a domain (domain name) using the example of the Reghouse registrar
Buying a domain (domain name) using the example of the Reghouse registrar  Local server Denwer - how to create a website on a computer - installation, configuration and removal of Denver
Local server Denwer - how to create a website on a computer - installation, configuration and removal of Denver
What is the Hosts file for?
The purpose of this system file- assigning certain website addresses a specific IP.
This file is very popular with all kinds of viruses and malware in order to write their data into it or simply replace it.
The result of these actions may be signs of “insertion” of a site into browsers, which will ask to send an SMS when opening the browser, or blocking of various sites, at the discretion of the creators of the virus.
Where is the hosts file in windows?
For different versions OS Windows location host file s a little different:
Windows 95/98/ME: WINDOWS\hosts
Windows NT/2000: WINNT\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
Windows XP/2003/Vista/Seven(7)/8: WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
Moreover, the ending hosts, it already is final file, not a folder. He doesn't have it.
What it should look like correct file hosts?
The "contents" of the hosts file are also slightly different for different versions windows, but not really. It is "written" in English why it is needed and how to make exceptions with one example. All lines starting with a # sign mean that they are commented out and do not affect the file.
Contents of the original hosts file for Windows XP:
#
#
#space.
#
#
# For example:
#
127.0.0.1 localhost
Contents of the original hosts file for Windows Vista:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2006 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
127.0.0.1 localhost::1 localhost
Contents of the original hosts file for Windows 7:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handle within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhost
Contents of the original hosts file for Windows 8:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhost
As you can see, the contents of the host file for different windows versions, there are no special differences.
How to open and edit the hosts file?
The hosts file can be standard Notepad Windows.
This is probably the most interesting part of the article.
First of all, you need to understand why change this file at all? Yes, in order to deny access to certain sites. Thus, by changing this file and writing the site address into it, the user will not be able to access it through any .
In order to change the hosts file, it is advisable to open it as administrator () by right-clicking on the file and selecting "Run as administrator". Or open Notepad this way and open the file in it.
For quick action, you can simply click the Start button and select Run ( win+r) () and enter in the line:
notepad %windir%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts

As a result, this file will open in Notepad.
In order to block access to the site(let's assume it will be test.ru), you just need to add a line with this site at the very bottom:
127.0.0.1 test.ru
As a result, the file will have the following content:
# Copyright (c) 1993-1999 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# This HOSTS file created by Dr.Web Anti-rootkit API
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhost
127.0.0.1 test.ru
Every new site you want to block must start with new line and register, not forgetting the local IP address 127.0.0.1
Also, to edit the hosts file, there is a program HOSTS EDITOR, which you can download and read the description from.
The way it works is that it helps edit the hosts file.
From the screenshot below the principle of its operation is clear; everything is done in a couple of clicks. Adding is done by clicking on +.

After editing, do not forget to click on the save button (2 button “Save changes” to the left of the “+” button).
You can also change this file for good purposes, for example speed up site loading.
How does this work?
When you visit a site, you see its domain name, which has letters. But all sites on the Internet have an IP address, and names are already assigned using DNS. I won’t go into details of this process; that’s not what the article is about. But here you need to know that the hosts file has priority when accessing sites, and only after it does a request to DNS occur.
In order to speed up the loading of a site, you need to know its IP address and domain.
The IP address of the site can be found using various services, for example or .
A domain is the name of a website.
For example, let's speed up the loading of this site where you are reading an article by explicitly specifying the IP address and domain to the file.
Then the added line will be:
91.218.228.14 website
This speeds up page loading in a couple of seconds, and sometimes can give access if standard means You cannot access the site.
Still possible redirect to another site using hosts file.
To do this, you need to know the IP address of the site and its domain (as in the case described above), then the added line will be like this:
91.218.228.14 test.ru
And now, after entering test.ru into the address bar of your browser, you will be redirected to the site specified in the IP address..
If you want clean hosts file, then you can do this by simply deleting the content and pasting into it original text, from the description above (under spoilers).
Some nuances in the hosts file:
This way you can easily and free of charge block access to sites in Windows by editing the hosts file.
The hosts file is designed to match domain names (sites), which are written using symbols, and the corresponding IP addresses (for example, 145.45.32.65), which are written as four numerical values. You can open any website in your browser not only after entering its name, but also after entering the IP address of this site.
IN Windows request to the hosts file has priority over requests to DNS servers. At the same time, the contents of this file are controlled by the computer administrator himself.
Therefore, quite often malware tries to change the contents of the hosts file. Why are they doing this?
They do this to block access to popular sites, or to redirect the user to other sites. There, at best, he will be shown an advertisement, and at worst, a fake page of a popular resource will be opened (social network, email service window, online banking service, etc.), asking him to enter data from his account.
Thus, due to the user's carelessness, an attacker can gain access to the user's data and cause damage to him.
Where is the hosts file located?
The hosts file is located in the folder with the Windows operating system, usually the “C” drive on the user’s computer.
The path to the hosts file will be like this:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
You can manually go through this path, or immediately open the folder with the host file using a special command.
For quick access to the file, press the keyboard shortcut “Windows” + “R”. This will open the Run window. In the "Open" field, enter either the path to the file (see above) or one of these commands:
%systemroot%\system32\drivers\etc %WinDir%\System32\Drivers\Etc

This file has no extension, but can be opened and edited in any text editor.
Standard contents of the hosts file
In the Windows operating system, the "hosts" file has the following standard contents:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp. # # This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows. # # This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each # entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should # be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name. # The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one # space. # # Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual # lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol. # # For example: # # 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server # 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host # localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself. # 127.0.0.1 localhost # ::1 localhost
This file is similar in content to the operating systems Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10.
All entries that begin with the hash character # and continue to the end of the line are largely irrelevant to Windows, since they are comments. These comments explain what the file is for.
It says here that the hosts file is designed to map IP addresses to site names. Entries in the hosts file will need to be made according to certain rules: each entry must begin on a new line, the IP address is written first, and then the site name after at least one space. Next, after the hash (#), you can write a comment to the entry inserted into the file.
These comments do not affect the operation of the computer in any way, you can even delete all these entries, leaving only an empty file.
You can download the standard hosts file from here to install on your computer. It can be used to replace the modified file if you don't want to edit the hosts file on your computer yourself.
What to pay attention to
If the file on your computer is no different from this one, standard file, this means that there are no problems that could arise due to the change this file There are no malware on your computer.
Pay special attention to the contents of the file, which are located after these lines:
# 127.0.0.1 localhost # ::1 localhost
The host file can be inserted additional entries, which are added here by some programs.
For example, in this image, you can see that the program has added some entries to the standard contents of the hosts file. Between the commented lines, additional entries were inserted to perform certain actions. This was done so that during the installation of programs on my computer, this utility cut off unwanted software.

There may be additional lines, this type: first a “set of numbers”, and then after a space, “site name”, added in order, for example, to disable advertising in Skype program, or block access to a site.
If you yourself have not added anything to the hosts file, and do not use the program mentioned in this article (Unchecky), then you can safely remove incomprehensible entries from the hosts file.
Why do they change the hosts file?
The hosts file is modified in order to block access to a certain resource on the Internet, or in order to redirect the user to another site.
Usually, initially malicious code is executed after launching a program downloaded from the Internet. At this point, changes are automatically made to the properties of the browser shortcut, and quite often additional lines are added to the hosts file.
To block a site (for example, the VKontakte site), lines of this type are entered:
127.0.0.1 vk.com
For some sites, two versions of the site name may be entered with “www” or without this abbreviation.
You yourself can block unwanted sites on your computer by adding a similar entry to the host file:
127.0.0.1 site_name
In this entry, the IP address (127.0.0.1) is the network address of your computer. Next comes the name of the site that you need to block (for example, pikabu.ru).
As a result, after entering the site name, you will see a blank page from your computer, although the name of this web page will be written in the address bar of the browser. This site will be blocked on your computer.
When using redirection, after entering the name of the desired site, a completely different site will be opened in the user’s browser, usually this is a web page with advertising, or a fake page of a popular resource.
To redirect to another site, entries of the following type are added to the host file:
157.15.215.69 site_name
In the beginning recruitment is underway numbers - IP address (I wrote here random numbers for example), and then, after a space, in Latin letters the name of the site will be written, for example, vk.com or ok.ru.
The way this method works is something like this: bad people deliberately create a fake (fake) website with a dedicated IP address (otherwise this method will not work). Next, an infected application gets onto the user’s computer, and after launching it, changes are made to the hosts file.
As a result, when a user types the name of a popular site in the address bar of the browser, instead of the desired site, he is redirected to a completely different site. This could be a fake social network page that is designed to steal user personal data, or a website with intrusive advertising. Very often, from such a fake site, there are redirects (redirections) to many other specially created pages with advertising.
How to edit the hosts file
You can change the contents of the host file yourself by editing it using text editor. One of the most simple ways To be able to change the file, open the hosts file in Notepad, opening the program as administrator.
To do this, create a shortcut to the Notepad utility on the Desktop, or launch the application in standard programs, which are located in the Start menu. To start, first click on the program shortcut with the right mouse button, and then select in context menu"Run as administrator" item. After this, the Notepad text editor window will open.
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
After opening the "etc" folder, you will not see the "hosts" file, since Explorer will be selected to display text files. Select the All Files setting. After this, the hosts file will be displayed in this folder. You can now open the hosts file in Notepad to edit it.
After editing is complete, changes to the hosts file. Please note that the file type when saving should be “All files”.
Conclusions of the article
In the event that malware changed the entries in the hosts file, you can replace the modified file with a standard one, or edit the contents of this file, removing unnecessary entries from there.
How to change the hosts file (video)
Senior Technology Writer
Someone sent you a email ETC file and you don't know how to open it? Maybe you found an ETC file on your computer and were wondering what it was? Windows may tell you that you cannot open it, or in the worst case, you may encounter a corresponding error message associated with the ETC file.
Before you can open an ETC file, you need to find out what type of file the ETC file extension is.
Tip: Incorrect ETC file association errors can be a symptom of other underlying issues within your Windows operating system. These invalid entries can also produce associated symptoms such as slow Windows startups, computer freezes, and other PC performance issues. Therefore, it is highly recommended that you scan your Windows registry for invalid file associations and other issues related to a fragmented registry.
Answer:
ETC files have Uncommon Files, which is predominantly associated with eTreppid Compressed File.
ETC files are also associated with Seismograph File and FileViewPro.
Additional types of files may also use the ETC file extension. If you are aware of any other file formats that use the ETC file extension, please contact us so we can update our information accordingly.
How to open your ETC file:
The fastest and easy way Opening your ETC file means double-clicking on it. IN in this case Windows system she will choose the necessary program to open your ETC file.
In case your ETC file does not open, it is very likely that the necessary software is not installed on your PC. application program to view or edit files with ETC extensions.
If your PC opens the ETC file, but it's the wrong application, you'll need to change your file association settings. Windows registry. In other words, Windows associates ETC file extensions with the wrong program.
Install optional products - FileViewPro (Solvusoft) | | | |
ETC File Analysis Tool™
Not sure what type the ETC file is? Do you want to get precise information about a file, its creator and how it can be opened?
Now you can instantly get all necessary information about the ETC file!
Revolutionary ETC File Analysis Tool™ scans, analyzes and reports detailed information about the ETC file. Our patent-pending algorithm will quickly analyze the file and provide detailed information within seconds in a clear, easy-to-read format.†
In just a few seconds, you'll know exactly what type of ETC file you have, the application associated with the file, the name of the user who created the file, the file's protection status, and other useful information.
To begin your free file analysis, simply drag-and-drop your ETC file inside the dotted line below, or click "Browse My Computer" and select your file. The ETC file analysis report will be shown below, right in the browser window.
![]()
Drag the ETC file here to start analysis
View my computer »
Please also check my file for viruses
Your file is being analyzed... please wait.
