In Dune the volume label is like a hard drive. How to format a hard drive: methods
In some cases, you may need to rename the drive in Windows 7. This is usually done for more comfortable PC management, for example, you can set a label indicating that the drive is intended for archival copies of important data.
Important! In Windows 7, you can also change the letter of non-system partitions, but before performing these actions, you must consider the possible risks.
Changing the volume label
Users treat their PCs differently. Some are quite satisfied with the default parameters offered by the system, others prefer to “customize” the system for themselves, achieving the most comfortable conditions for using the computer.
After installation, all partitions on the hard drive are often named “Local Disk,” but it is much more convenient to designate the space allocated for movies, photos, or backups more clearly.
This is especially true if the PC is used by several users.
A volume label is a descriptive name for a partition on a hard drive; it is necessary only for user convenience and does not affect the operation of the OS.
- Let's look at the main ways to change the volume label:
- use of a graphical interface;

label command.
Most users are not used to working with command-based systems. For them, changing the volume label using a GUI is much more suitable.
- Here is the procedure for changing the volume label:
- open “My Computer”;
- right-click to open the menu on the desired drive;
- select “Rename”;
- enter a new name;

press Enter.
- Before changing the volume label, you need to know the basic requirements for it, because otherwise proper operation may be disrupted, consider them:
- maximum label length is 11 characters for FAT or 32 for NTFS;
- spaces are allowed;
- It is prohibited to use a tab character in a label;
The label of a disk formatted in FAT cannot contain the following characters: * ? / | . , ; : + = ".
Hard drives have usually been formatted in NTFS for many years now; other drives may still be formatted in the older FAT file system.
It is more convenient for experienced users to change the volume label using the command line and the label command.
- Let's look at how to change the label from the command line:
- open a command prompt with administrator rights;
- enter the command label drive letter;
- specify a new label and confirm the entry using the Enter key.
Please note that the old label will be erased without displaying an additional warning.

If you just need to remove the volume label, you need to do the following:
- run command line with administrator rights;
- type the command label drive letter and press Enter;
- when prompted, leave the input field blank and press Enter;
- Confirm deleting the mark by pressing Y.
Possible problems
Sometimes Windows 7 users cannot change the drive name. This is due to the big changes that have occurred in this version of the OS. Often on computers with Vista and XP, to prevent infection by certain viruses, an autorun.inf file was created in the root of the disk. In Windows 7 there is no point in creating it, but this file may be hidden.

Let's look at how to enable the display of hidden files:
- open “Control Panel”;
- go to the “Folder Options” section;
- on the “View” tab, check the box next to “Show hidden files and folders”;
- Click Ok.
You can now delete the autorun.inf file and restart the computer, after which you can change the volume label.
Video: How to change the drive letter
Changing the drive letter
The drive letter is a pointer directly to the logical partition of the hard drive; it is also found in removable drives, CD/DVD drives, and virtual disks. Sometimes you may need to change it for greater convenience or to correctly transfer programs to the installed new drive.
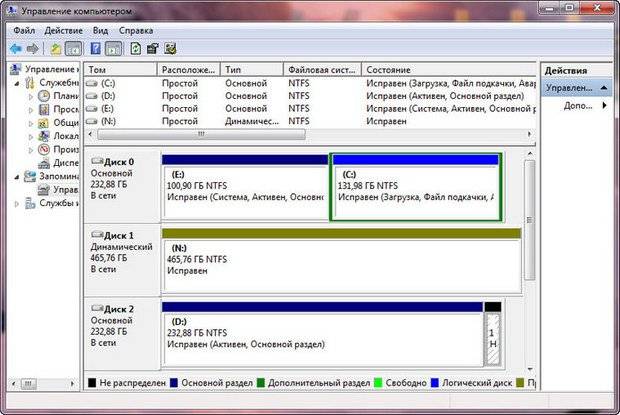
Important! Never try to change the letter of a system drive. In most cases, this operation will fail, and in some cases there will be problems starting the OS.
Let's look at how to change the drive letter:
- go to “Control Panel”;
- select “Computer Management” and go to the “Disk Management” section;
- On the partition that needs to change the letter, right-click;
- in the menu that opens, select “Change drive letter or drive path”;
- in the window that appears, click on the “Change” button;
- choose the appropriate letter;
- click Ok;
- confirm the changes.
Important! Changing the drive letter can have unpredictable effects on installed applications. It is also not recommended to change the drive letter for the optical drive, as Nero and some other programs may not work correctly after this.
You can change the hard drive label an unlimited number of times, since it is only for the convenience of users and does not affect running applications. Changing the drive letter is recommended only for experienced PC owners, as these actions can harm the system.
>A volume label is a special configuration used to create hard disk volumes. Changing it is not recommended because you may lose some user files.
Instructions
Question from a user
Hello.
I want to completely delete all content on the disk, and then reinstall the system. I have two drives ("C:" and "D:") - I was able to format one, but there is a problem with the "C:" drive. Can you tell me how I can format the system hard drive (on which Windows 8 is installed)?
Good day to all!
In general, on today’s modern system, formatting a disk is not a difficult operation, I would even say simple (not like it was 20 years ago). Perhaps, questions arise only in cases where Windows does not see the disk, errors appear during formatting, or when trying to format the system disk (as in your case).
In the article below I will discuss several formatting methods - depending on your tasks and the specific problem, choose the one you need. So...
Important: After formatting the drive, all information on it will be deleted! Make a copy of the necessary files from the disk to third-party media in advance.
From under Windows
Via My Computer
Probably the classic and easiest way to format a disk is to go to “My Computer” (or “This Computer”, depending on the version of your OS), and find the desired disk partition in it. Then select this section, right-click on it - and select the required one in the context menu (ie formatting, see screenshot below).
Note: if the "My Computer" icon is not on the desktop, and you do not know how to open it, press the button combination WIN+E- Explorer will open: in the menu on the left, select the link to “My Computer/This Computer”.

Format disk // This PC // Windows 10
- file system: FAT 32, NTFS, exFAT, etc. In most cases, the best option for a hard drive is to use NTFS;
- allocation unit size: 4096 bytes (optimal);
- volume label: disk name, you can enter any (I recommend using the Latin alphabet, as some programs do not read Russian font correctly).

In general, the default settings will usually suit most users - you can immediately click the "Get Started" button. In a few minutes you will receive a “clean” disk...
Via Disk Management
In cases where you go to “My Computer” - and it simply does not show your connected disk (this often happens with new disks that have not been formatted) - then you need to use either special utilities or use the “disk management” tool , built into Windows.
To open Disk Management you need to:
- press a combination of buttons WIN+R to open the Run window;
- enter the command diskmgmt.msc and press Enter. The Disk Management application should open.
Next, you will see not only all connected disks, flash drives, memory cards, etc., but also what partitions were created on them - i.e. the entire structure. Select the desired section and right-click on it - in the context menu, click on the item "Format..." (see red arrows in the screenshot below).


Via command line
In cases where Explorer freezes (for example), also in the event of various types of errors, you can try formatting the disk through the command line.
First you need to open it as an administrator. For this:

format G: /FS:NTFS /q
G: - letter of the drive to be formatted (specify carefully!);
/FS:NTFS - select a file system;
/q - quick formatting.

Basically, the disk must be formatted.
In Windows 10, by the way, a small “error” may appear - the system will ask you to specify the volume label for the disk, and then write that “The specified disk label is invalid” (although you seem to have specified everything correctly, example below).

In this case, do the following...
First, open the drive you want to format in a command prompt, for example, drive G: (see screenshot below).

Team VOL- look at the volume label
Next, enter the formatting command again, and in the disk label field - the label that we found out in the previous step (in my case - Windows 8). Next, you will be warned that all data will be destroyed during formatting (you agree by entering y and pressing Enter ).
In the next step you will be prompted to enter a volume label - now you can enter any name (32 characters). You can simply leave the field empty by pressing Enter. Actually, that’s it - the disk will be formatted (screenshot below).

With the help of special utilities
The best programs and utilities for working with a hard drive:
There are now hundreds of different programs and utilities for working with hard drives. Operations such as formatting, partitioning, defragmentation, etc. can be done in more convenient programs than those built into Windows. The link to the article with the best of them is given above.
In my opinion, one of those that deserves attention is AOMEI Partition Assistant.
AOMEI Partition Assistant
It allows you to quickly, safely, and easily carry out the most necessary operations with disk drives:
- change their partition size (including without formatting);
- move partitions;
- merge sections;
- format drives;
- change labels and much more!
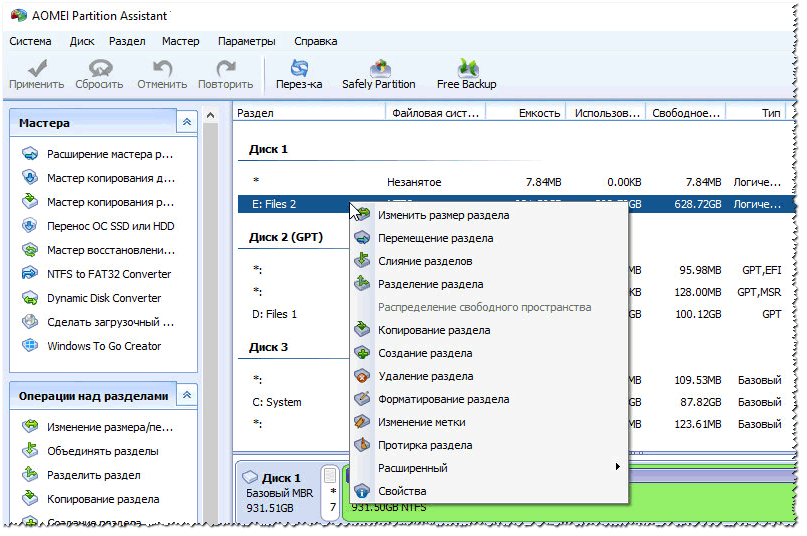
What’s also captivating is that the program has many different step-by-step wizards - they will help solve the problem even for those users who have only recently become acquainted with a PC. Well, for example, you can convert the FAT 32 file system to NTFS without losing data, transfer Windows from a hard drive to a newfangled SSD, etc.
Via BIOS
(for formatting system partitions, for example, on which Windows is installed)
If you want to format a partition on which Windows is installed, you won’t be able to do it just like that. The bottom line is that you need to boot from another medium - for example, from another hard drive (on which Windows is installed) or from a bootable USB flash drive, and then format your disk.
Naturally, you need to prepare such media in advance (for example, an installation flash drive with Windows) - since after formatting the system partition of the drive, Windows will no longer boot from it (don’t install it again yet. I explained it chaotically, but in general terms, I think it’s clear ☻).
Using a Windows installation flash drive
The easiest way to format the system partition of a disk is to use a Windows installation flash drive. You can learn how to create and prepare it (if you don’t have one) from my previous articles (links are provided below).
Utilities for creating bootable USB flash drives with Windows -
Creating a bootable Windows 10 USB flash drive -
Creating a bootable USB flash drive for installing Windows XP, 7, 8, 10 (UEFI and Legacy) -
The easiest way to boot from a flash drive is to use a special boot menu - BOOT MENU, which can be called up immediately after turning on the computer/laptop (or by changing the boot priority in the BIOS). In order not to repeat myself here, I will provide a couple of links to detailed articles about this.
Hot keys to enter the BIOS menu, Boot Menu, recovery from a hidden partition -
How to configure the BIOS to boot from a flash drive or disk (CD/DVD/USB) -
Next, after booting from the installation flash drive, you need to go to selecting a partition for installing Windows. In this step, you can format both the entire disk (delete all partitions and create them again), as well as its individual partitions.

If you have difficulties and you don’t know how to get to this step when installing Windows, I recommend reading this article:
With the help of special programs
Take the same AOMEI Partition Assistant that I recommended using when working under Windows, just above in the article. She has an excellent tool in her arsenal for creating a special emergency flash drive from which you can boot when your system crashes (or it is not installed on the disk at all).
I have an article on programs for working with hard drives on my blog:(including information about AOMEI Partition Assistant).
To create such a flash drive, you need to run the program on your working PC "Master/Make Bootable CD Master".


To boot from such a flash drive, use also Boot Menu, links to instructions were given above in the article, in the previous step. When you boot from the emergency flash drive, the menu and operation of the program will be similar to that running under Windows. Also click on the desired disk and perform the necessary operation (screenshot below).

AOMEI Partition Assistant - formatting a partition
That's all, a separate merci for additions.
Users often think about which file system is best to format a flash drive. Usually they choose the system that they like best, however, there are still a few tips. Fat32 It works faster, but such a drive cannot accommodate a file larger than 4 GB. If you use the drive to store small files and documents, it would be better NTFS. In case of storing large files, such as videos or images, it is better to use exFAT. Experiments have shown that in these cases such file systems cope best.
As an exception, it can be noted that some equipment requires drives with a certain system; in this case, you will still have to format it to meet these requirements. Typically, older or specialized equipment requires fat32, while others can use file systems at the discretion of the manufacturer.
Do I need to format a new flash drive?
There is usually no need to format a new drive. All of them now work right out of the box, you just need to unpack and connect to your computer. However, formatting will also not do any harm, because there is no information on the flash drive and nothing will be damaged. The user just needs to check which file system is on the flash drive at the moment. It often happens that this is fat32, which means that it will not be possible to record large files. If this situation does not suit you, then you should re-encode the flash drive while there is no information on it.
Volume label for disk when formatting ntfs
Volume label made easy drive name. It will be visible when you connect the drive to your computer. It’s worth changing the standard name of the flash drive so that you can immediately find yours and not get confused among many identical ones. Typically, media are named by manufacturer and model number, however, nothing prevents the user from coming up with something of his own.
To change the label, the easiest way is to go into your computer, right-click on the flash drive and select rename. After this, you can enter the device name. However, lowercase will not be available here, so the user may not like it.
You can also set the device name in formatting process, indicating the name in the corresponding item indicated in the picture, after which the device will be renamed.
There is still an opportunity to use autorun file. To do this, you will need to create a text file in the root of the disk with the name autorun and save it with the extension .inf. In the file itself you should write Label =Flash drive name.
Many users block autorun because various malicious programs like to be registered there, so this method is not so reliable.
Do not forget about the restrictions that are imposed depending on the file system; if the requirements are not met, you may receive an error - “Invalid volume label specified.” For NTFS:
- Name no more than 32 characters
- No tab
- Uppercase and lowercase characters.
For FAT
- No more than 11 characters
- No tab
- Capital characters only
Formatting a flash drive to NTFS
This section will directly tell you how to format the drive into the desired file system.
The easiest way
In this case, the built-in Windows utility will be used. You should go into your computer, right-click on the flash drive and select “ Format». 
Required here choosentfs and here you need to specify the device name. Cluster size can be left standard. In general, a cluster is the minimum amount of space that can be allocated for a file. If you plan to carry a lot of small files, then you should choose a smaller size, and if large, then a larger one. However, in most cases, the standard cluster suits the majority. Followed by uncheck with quick formatting, if necessary, so that the data cannot be recovered. Then all that remains is to wait for the process to complete.
Using the Command Line
For formatting you should use operatorformat. The user will need to open the command line and enter the same command as in the picture, replacing E with the letter of his flash drive. 
The format operator is written as FORMAT volume
Options:
- volume– letter of the drive to be formatted.
- /FS:filesystem– FAT, FAT32, NTFS, or UDF is specified here.
- /V:label— Volume label.
- /Q- Quick formatting. When using it, there is no need for the /p parameter.
- /C— for NTFS, compression of all data on the new volume.
- /X– If there is a need to disable all access to the drive, then you should enter this parameter.
- /R:edition- only for UDF.
- /D- UDF only.
- /A:size— Replaces the default cluster size, discussed above.
Formatting via Disk Management
You can right-click on the computer and select Manage, then go to disk management. Here you should select a flash drive, also right-click on it and select Format, after which all that remains is to configure everything and wait for the process to complete. 
Using the diskpart utility
You can also use another command that is available on the command line. Enter one by one:

Using USB Disk Storage Format Tool
To get started, you should download and run the program. IN fieldDevice You will need to select the desired flash drive, and then specify its name and cluster. Then all you have to do is press start and wait for formatting to finish. If you need quick formatting, you should check this box; the program is slightly different from the standard one. 
Convert flash drive to NTFS
You don't have to completely erase the media, but simply convert it from one file system to another. To do this, launch the command line and enter the operator convert h: /fs:ntfs /nosecurity /x, replace h with the drive letter.  There must be free space on the flash drive to complete the process, otherwise you may receive an error message. Also, just in case, you should copy all the data.
There must be free space on the flash drive to complete the process, otherwise you may receive an error message. Also, just in case, you should copy all the data.
The most important information about a disk is the amount of free and used space. To obtain this information, open the My Computer window by double-clicking the My Computer icon, then right-clicking on the icon of the desired drive and selecting Properties from the context menu. The General tab indicates the amount of free and used space on the disk, volume label, disk type and file system.
What is a volume label?
A volume label is an alphanumeric mark of up to 11 characters (up to 32 characters in NTFS) indicating the name of the disk. This label appears along with the drive icon. Having a drive label is not necessary, but it often helps when organizing floppy or removable drives.
How do I change the volume label?
After opening the My Computer window by double-clicking on the My Computer icon, right-click on the icon of the desired drive and select Properties from the context menu. On the General tab, you can enter the volume label in the field at the top of the window. In addition, the volume label can be set when formatting the disk.
14.4. File systemWindows 7 ( kb.chemtable.com/ru/ windows-7 -file- system.htm )
Windows 7 uses a file system NTFS, which, today, is one of the most common in the world.
The basis of NTFS is MFT (Master File Table). In essence, it is a file of a special format, which is located in a special MFT zone of the partition. This zone is accessible only to operating system service tools or special utilities that access the hard drive directly. MFT presents a table that lists all files with basic attributes and security settings. But not only. For each file, MFT stores the addresses of the sectors in which its contents are located. This is very important information, because without it, the system simply would not know where the requested object is located and where the reading head of the hard drive needs to be moved.
In Windows 7, there are a number of folders called service folders. By default, they are the same for all users of this OS. It is advisable not to touch some of them, as this can lead to malfunctions in Windows 7. The content of others can be changed without any fear.
Without a doubt, this is the most important folder located on the active partition of the hard drive. It stores all executable files of the operating system, drivers, modules, etc. Therefore, deleting anything from this folder is strictly not recommended. It is worth noting that in some cases it may have a different name.
Windows.old
Folder with the old operating system. Occurs on the hard drive if Windows 7 was installed without formatting it. For the vast majority of users, it is not needed, and therefore can be removed completely calmly.
Folder for storing user profiles. By default, it is located in the root of the disk with the operating system. Contains a number of standard folders, as well as one folder for each account. They contain “user” subfolders, including Desktop, Documents, Pictures, Favorites, etc. Their contents depend entirely on the person. Other subfolders are used to store service information of various applications, browsers, etc.: AppData, ApplicationData, Cookies, Local Settings, etc. They are hidden and it is not recommended to change their contents manually.
The folder that contains all operating system boot files. It is hidden and should not be changed.
ProgramData
Another very important hidden folder. It is where applications installed on the operating system store their data, installation files, etc. Naturally, there is no need to remove anything from it.
Recovery
The folder in which the image required to enter the recovery environment is stored. Again, it is hidden and cannot be changed.
$Recycle.Bin
Essentially, this folder is the Windows Recycle Bin. This is where all deleted information is moved. The folder is hidden, however, you can delete both it and its contents. In essence, this will be tantamount to emptying the Trash or part of it. Please note that each hard drive partition has its own $Recycle.Bin folder, which stores files deleted from it.
