The WannaCry ransomware virus has blocked your PC! How to protect yourself from infection? How to protect yourself from the Petya ransomware virus
Good afternoon, dear readers and guests of the blog, as you remember in May 2017, a large-scale wave of infection of computers with the Windows operating system began with a new ransomware virus called WannaCry, as a result of which it was able to infect and encrypt data on more than 500,000 computers , just think about this figure. The worst thing is that this type of virus is practically not caught by modern antivirus solutions, which makes it even more threatening. Below I will tell you a method on how to protect your data from its influence and how to protect yourself from ransomware in a minute, I think you will find it interesting.
What is a ransomware virus?
A ransomware virus is a type Trojan horse, whose task is to infect workstation user, identifying files on it required format(for example, photos, audio recordings, video files) their subsequent encryption with a change in file type, as a result of which the user will no longer be able to open them, without special program decoder. It looks like this.

Encrypted file formats
The most common file formats after encryption are:
- no_more_ransom
- vault
Consequences of a ransomware virus
I will describe the most common case in which an encoder virus is involved. Let's imagine an ordinary user in any abstract organization, in 90 percent of cases the user has the Internet at his workplace, since with the help of it he brings profit to the company, he surfs the Internet space. A person is not a robot and can be distracted from work by looking at sites that interest him, or sites that were recommended to him by his friend. As a result of this activity, he can infect his computer with a file encryptor without knowing it and find out about it when it is already too late. The virus has done its job.
The virus, at the time of its operation, tries to process all the files to which it has access, and this is where it begins that important documents in the department folder to which the user has access suddenly turn into digital garbage, local files and much more. It is clear that there should be backup copies of file shares, but what to do with local files, which can amount to a person's entire work, as a result the company loses money for idle work, and the system administrator leaves his comfort zone and spends his time decrypting files.
The same may happen to an ordinary person, but the consequences here are local and concern him and his family personally. It’s very sad to see cases where a virus has encrypted all files, including family photo archives, and people have no backup copy, well, it’s not common among ordinary people users to do it.
With cloud services, everything is not so simple, if you store everything there and do not use a thick client in your Windows operating system, it’s one thing, 99% of the time nothing threatens you there, but if you use, for example, Yandex disk or " mail Cloud"by synchronizing files from your computer to it, then if you get infected and receive that all the files are encrypted, the program will send them straight to the cloud and you will also lose everything.
As a result, you see a picture like this, where you are told that all files are encrypted and you need to send money, now this is done in bitcoins so as not to identify the attackers. After payment, they should supposedly send you a decryptor and you will restore everything.
Never send money to criminals

Remember that not a single modern antivirus today can provide Windows protection against ransomware, for one simple reason that this Trojan does not do anything suspicious from its point of view, it essentially behaves like a user, it reads files, writes, unlike viruses, it does not try to change system files or add registry keys, which is why its detection is so difficult, there is no line distinguishing it from the user
Sources of ransomware trojans
Let's try to highlight the main sources of the encryptor's penetration into your computer.
- Email > very often people receive strange or fake emails with links or infected attachments, upon clicking on which the victim begins to have a sleepless night. I told you how to protect email, I advise you to read it.
- Through software- you downloaded the program from unknown source or a fake site, it contains an encoder virus, and when you install the software, you add it to your operating system.
- Through flash drives - people still very often visit each other and transfer a bunch of viruses through flash drives, I advise you to read “Protecting a flash drive from viruses”
- Via IP cameras and network devices having access to the Internet - very often, due to incorrect settings on a router or IP camera connected to a local network, hackers infect computers on the same network.
How to protect your PC from ransomware
Protects against ransomware proper use computer, namely:
- Do not open mail you do not know and do not follow unknown links, no matter how they reach you, be it mail or any of the messengers
- Install updates to the Windows or Linux operating system as quickly as possible; they are released not so often, about once a month. If we talk about Microsoft, then this is the second Tuesday of every month, but in the case of file encryptors, updates may be abnormal.
- Do not connect unknown flash drives to your computer, ask your friends to send better link to the cloud.
- Make sure that if your computer does not need to be accessible in local network for other computers, then turn off access to it.
- Limit access rights to files and folders
- Installing an antivirus solution
- Do not install incomprehensible programs hacked by someone unknown
Everything is clear with the first three points, but I will dwell on the remaining two in more detail.
Disable network access to your computer
When people ask me how protection against ransomware is organized in Windows, the first thing I recommend is that people disable the “File and Printer Access Service” Microsoft networks", which allows other computers to access resources of this computer using Microsoft networks. This is also relevant from curious system administrators working for your provider.
Disable this service And protect yourself from ransomware in a local or provider network, as follows. Press the key combination WIN+R and in the window that opens, execute, enter the command ncpa.cpl. I'll show this on my test computer running Windows 10 Creators Update.

Select the one you need network interface and click on it right click mice, from context menu select "Properties"
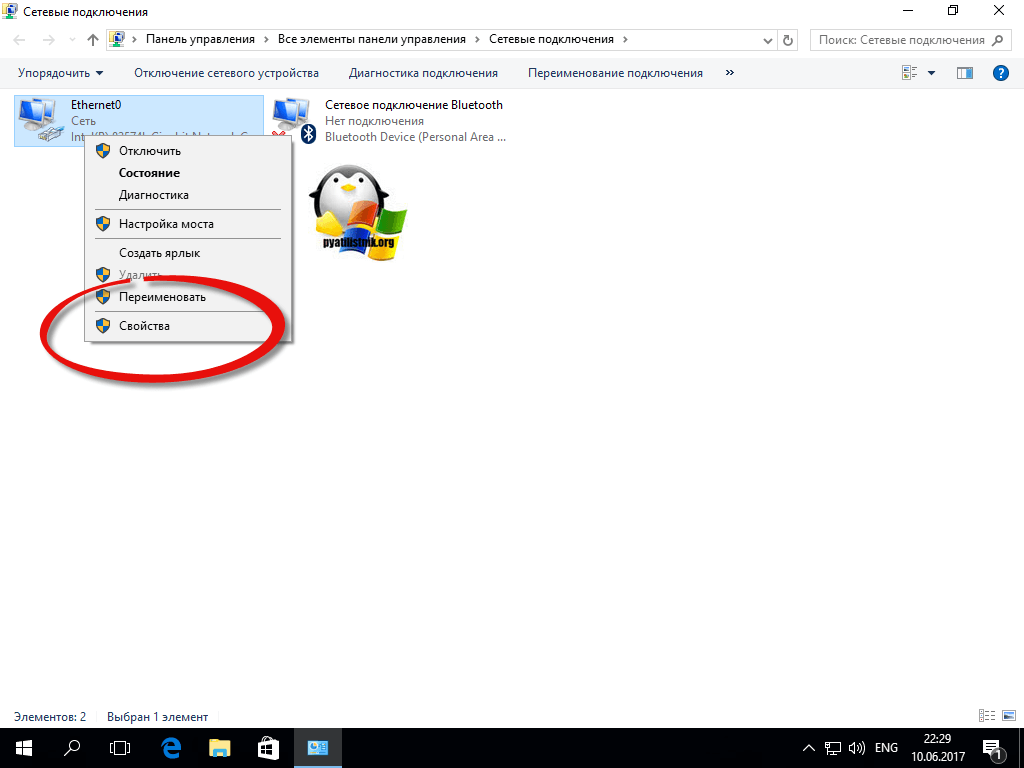
We find the item “File and printer sharing for Microsoft networks” and uncheck it, then save, all this will help protect your computer from a ransomware virus on the local network; your workstation will simply not be accessible.

Restricting access rights
Protection against ransomware virus in Windows can be implemented like this in an interesting way, I'll tell you how I did it for myself. And so the main problem in the fight against encryptors is that antiviruses simply cannot fight them in real time, well, they cannot protect you at the moment, so we will be more cunning. If the encryptor virus does not have write rights, then it will not be able to do anything with your data. Let me give you an example, I have a photo folder, it is stored locally on the computer, plus there are two backup copies on different hard drives. On your own local computer I made rights to it, read only, for that account under which I sit at the computer. If the virus had gotten in, it simply wouldn’t have had enough rights, as you can see, everything is simple.
How to implement all this in order to protect yourself from file encryptors and protect everything, we do the following.
- Select the folders you need. Try to use folders; they make it easier to assign rights. Ideally, create a folder called read-only, and place all the files and folders you need in it. The good thing is that by assigning rights to the top folder, they will automatically be applied to other folders in it. Once you have copied everything necessary files and folders in it, go to the next step
- Right-click on the folder from the menu and select "Properties"

- Go to the "Security" tab and click the "Edit" button

- We try to delete access groups, if we receive a warning window that “The group cannot be deleted because this object inherits permissions from its parent,” then close it.

- Click the "Advanced" button. In the item that opens, click "disable inheritance"

- When asked "What do you want to do with the current inherited permissions" select "Remove all inherited permissions from this object"

- As a result, everything in the "Permissions" field will be deleted.

- Save the changes. Please note that now only the owner of the folder can change permissions.

- Now on the "Security" tab, click "Edit"

- Next, click "Add - Advanced"

- We need to add the group "Everyone", to do this, click "Search" and select the desired group.

- For Windows protection from the ransomware, you should have permissions set for the “Everyone” group, as in the picture.

- Now no encryptor virus will threaten you for your files in this directory.

I hope Microsoft and others antivirus solutions will be able to improve their products and protect computers from ransomware before they operate maliciously, but until this happens, follow the rules that I described to you and always make backup copies of important data.
It continues its oppressive march across the Internet, infecting computers and encrypting important data. How to protect yourself from ransomware, protect Windows from ransomware - have patches been released to decrypt and disinfect files?
New ransomware virus 2017 Wanna Cry continues to infect corporate and private PCs. U Damage from virus attack totals $1 billion. In 2 weeks, the ransomware virus infected at least 300 thousand computers, despite warnings and security measures.
Ransomware virus 2017, what is it?- as a rule, you can “pick up” on seemingly the most harmless sites, for example, bank servers with user access. Once on HDD victims, the ransomware “settles” in system folder System32. From there the program immediately disables the antivirus and goes into "Autorun"" After every reboot, ransomware runs into the registry, starting his dirty work. The ransomware begins to download similar copies of programs like Ransom and Trojan. It also often happens ransomware self-replication. This process can be momentary, or it can take weeks until the victim notices something is wrong.
The ransomware often disguises itself as ordinary pictures, text files , but the essence is always the same - this is an executable file with the extension .exe, .drv, .xvd; Sometimes - libraries.dll. Most often, the file has a completely harmless name, for example “ document. doc", or " picture.jpg", where the extension is written manually, and the true file type is hidden.
After encryption is complete, the user sees, instead of familiar files, a set of “random” characters in the name and inside, and the extension changes to a previously unknown one - .NO_MORE_RANSOM, .xdata and others.
Wanna Cry ransomware virus 2017 – how to protect yourself. I would like to immediately note that Wanna Cry is rather a collective term for all encryption viruses and ransomware, since Lately infected computers most often. So, we'll talk o s Protect yourself from Ransom Ware ransomware, of which there are a great many: Breaking.dad, NO_MORE_RANSOM, Xdata, XTBL, Wanna Cry.

How to protect Windows from ransomware. – EternalBlue via SMB port protocol.
Protecting Windows from ransomware 2017 – basic rules:
- Windows update, timely transition to a licensed OS (note: the XP version is not updated)
- updating anti-virus databases and firewalls on demand
- extreme care when downloading any files (cute “seals” can result in the loss of all data)
- backup important information onto removable media.
Ransomware virus 2017: how to disinfect and decrypt files.
Relying on antivirus software, you can forget about the decryptor for a while. In laboratories Kaspersky, Dr. Web, Avast! and other antiviruses for now no solution for treating infected files was found. On this moment It is possible to remove the virus using an antivirus, but there are no algorithms to return everything “to normal” yet.
Some try to use decryptors like the RectorDecryptor utility, but this won't help: an algorithm for decrypting new viruses has not yet been compiled. It is also absolutely unknown how the virus will behave if it is not removed after using such programs. Often this can result in the erasure of all files - as a warning to those who do not want to pay the attackers, the authors of the virus.
At the moment the most effective way getting back lost data means contacting technical support. support from the vendor of the antivirus program you use. To do this, you should send a letter or use the feedback form on the manufacturer’s website. Be sure to add the encrypted file to the attachment and, if available, a copy of the original. This will help programmers in composing the algorithm. Unfortunately, for many, a virus attack comes as a complete surprise, and no copies are found, which greatly complicates the situation.

Cardiac methods of treating Windows from ransomware. Unfortunately, sometimes you have to resort to full formatting hard drive, which entails a complete change of OS. Many will think of restoring the system, but this is not an option - even a “rollback” will get rid of the virus, but the files will still remain encrypted.

Encryptors (cryptolockers) mean a family malware, which, using various encryption algorithms, block user access to files on the computer (known, for example, cbf, chipdale, just, foxmail inbox com, watnik91 aol com, etc.).
Typically, the virus encrypts popular types of user files: documents, spreadsheets, 1C databases, any data sets, photographs, etc. File decryption is offered for money - the creators require you to transfer a certain amount, usually in bitcoins. And if the organization has not taken proper measures to ensure the safety of important information, transferring the required amount to the attackers may be the only way to restore the company’s functionality.
In most cases, the virus spreads through email, masquerading as quite ordinary letters: notifications from the tax office, acts and contracts, information about purchases, etc. By downloading and opening such a file, the user, without realizing it, runs malicious code. The virus sequentially encrypts the necessary files, and also deletes the original copies using guaranteed destruction methods (so that the user cannot recover recently deleted files using special tools).
Modern ransomware
Encryptors and other viruses that block user access to data are not new problem V information security. The first versions appeared back in the 90s, but they mainly used either “weak” (unstable algorithms, small key size) or symmetric encryption(files were encrypted with one key large number victims, it was also possible to recover the key by studying the virus code), or even came up with their own algorithms. Modern copies are free of such shortcomings; attackers use hybrid encryption: using symmetric algorithms, the contents of files are encrypted with very high high speed, and the encryption key is encrypted A symmetric algorithm. This means that to decrypt files you need a key that only the attacker owns, in source code I can't find the program. For example, CryptoLocker uses RSA algorithm with a key length of 2048 bits in combination with the symmetric AES algorithm with a key length of 256 bits. These algorithms are currently recognized as crypto-resistant.
The computer is infected with a virus. What to do?
It is worth keeping in mind that although ransomware viruses use modern encryption algorithms, they are not capable of instantly encrypting all files on a computer. Encryption occurs sequentially, the speed depends on the size of the encrypted files. Therefore, if you find while working that your usual files and programs no longer open correctly, you should immediately stop working on the computer and turn it off. This way you can protect some files from encryption.
Once you have encountered a problem, the first thing you need to do is get rid of the virus itself. We will not dwell on this in detail; it is enough to try to cure your computer using anti-virus programs or remove the virus manually. It is only worth noting that the virus often self-destructs after the encryption algorithm is completed, thereby making it difficult to decrypt files without turning to attackers for help. In this case antivirus program may not find anything.
The main question is how to recover encrypted data? Unfortunately, recovering files after a ransomware virus is almost impossible. By at least, guarantee full recovery In case of successful infection, no one will have any data. Many antivirus manufacturers offer their assistance in decrypting files. To do this, you need to send an encrypted file and Additional information(file with contacts of attackers, public key) through special forms, posted on the manufacturers' websites. There is a small chance that a way to fight a particular virus has been found and your files will be successfully decrypted.
Try using recovery utilities deleted files. It is possible that the virus did not use guaranteed destruction methods and some files can be recovered (this can especially work with files big size, for example, with files of several tens of gigabytes). There is also a chance to recover files from shadow copies. When using recovery functions Windows systems creates snapshots that may contain file data for the duration of the recovery point creation.
If your data was encrypted in cloud services, contact technical support or explore the capabilities of the service you use: in most cases, services provide a “rollback” function to previous versions files so they can be recovered.
What we strongly do not recommend doing is following the lead of ransomware and paying for decryption. There were cases when people gave money and did not receive the keys. No one guarantees that the attackers, having received the money, will actually send the encryption key and you will be able to restore the files.
How to protect yourself from a ransomware virus. Preventive measures
It is easier to prevent dangerous consequences than to correct them:
- Use reliable anti-virus tools and regularly update anti-virus databases. It sounds trivial, but this will significantly reduce the likelihood of a virus successfully injecting itself into your computer.
- Keep backup copies of your data.
This is best done using specialized backup tools. Most cryptolockers are able to encrypt backup copies, too, so it makes sense to store backup copies on other computers (for example, on servers) or on alienated media.
Limit permissions to change files in folders with backup copies, allowing only additional recording. In addition to the consequences of ransomware, backup systems neutralize many other threats associated with data loss. The spread of the virus once again demonstrates the relevance and importance of using such systems. Recovering data is much easier than decrypting it!
- Limit the software environment in the domain.
Another effective way to combat this is to restrict the launch of certain potentially dangerous file types, for example, with extensions .js, .cmd, .bat, .vba, .ps1, etc. This can be done using the AppLocker tool (in Enterprise editions) or SRP policies centrally in the domain. There are quite a few on the web detailed guides, how to do it. In most cases, the user will not need to use the script files listed above, and the ransomware will have less chance of successfully infiltrating.
- Be carefull.
Mindfulness is one of the most effective methods preventing the threat. Be suspicious of every letter you receive from unknown persons. Do not rush to open all attachments; if in doubt, it is better to contact the administrator with a question.
Alexander Vlasov, senior engineer of the information security systems implementation department at SKB Kontur
Modern technologies allow hackers to constantly improve methods of fraud in relation to ordinary users. As a rule, virus software that penetrates the computer is used for these purposes. Encryption viruses are considered especially dangerous. The threat is that the virus spreads very quickly, encrypting files (the user simply will not be able to open a single document). And if it’s quite simple, then it’s much more difficult to decrypt the data.
What to do if a virus has encrypted files on your computer
Anyone can be attacked by ransomware; even users who have powerful anti-virus software are not immune. File encrypting Trojans come in a variety of codes that may be beyond the capabilities of an antivirus. Hackers even manage to attack large companies in a similar way that have not taken care of necessary protection your information. So, having picked up a ransomware program online, you need to take a number of measures.

The main signs of infection are: slow work computer and changing document names (can be seen on the desktop).
- Restart your computer to stop encryption. When turning on, do not confirm the launch of unknown programs.
- Run your antivirus if it has not been attacked by ransomware.
- In some cases, shadow copies will help to restore information. To find them, open the “Properties” of the encrypted document. This method works with encrypted data from the Vault extension, about which there is information on the portal.
- Download the utility latest version to combat ransomware viruses. The most effective ones are offered by Kaspersky Lab.
Ransomware viruses in 2016: examples
When fighting any virus attack it is important to understand that the code changes very often, adding to new protection from antiviruses. Of course, security programs need some time until the developer updates the databases. We have selected the most dangerous encryption viruses of recent times.
Ishtar Ransomware

Ishtar is a ransomware that extorts money from the user. The virus was noticed in the fall of 2016, infecting a huge number of computers of users from Russia and a number of other countries. Distributed via email, which contains attached documents (installers, documents, etc.). Data infected by the Ishtar encryptor is given the prefix “ISHTAR” in its name. The process creates a test document that indicates where to go to obtain the password. The attackers demand from 3,000 to 15,000 rubles for it.
The danger of the Ishtar virus is that today there is no decryptor that would help users. Antivirus software companies need time to decipher all the code. Now you can only isolate important information(if they are of particular importance) to a separate medium, waiting for the release of a utility capable of decrypting documents. It is recommended to reinstall the operating system.
Neitrino

The Neitrino encryptor appeared on the Internet in 2015. The attack principle is similar to other viruses of a similar category. Changes the names of folders and files by adding "Neitrino" or "Neutrino". It is difficult to decrypt a virus - not all representatives of antivirus companies undertake this, citing very complex code. Restoration may help some users shadow copy. To do this, right-click on the encrypted document, go to “Properties”, “Previous Versions” tab, click “Restore”. It wouldn’t hurt to use free utility from Kaspersky Lab.
Wallet or .wallet.

The Wallet encryption virus appeared at the end of 2016. During the infection process, it changes the name of the data to “Name..wallet” or something similar. Like most ransomware viruses, it enters the system through attachments in emails sent by attackers. Since the threat appeared very recently, antivirus programs do not notice it. After encryption, he creates a document in which the fraudster indicates the email for communication. Currently, antivirus software developers are working to decipher the code of the ransomware virus. [email protected]. Users who have been attacked can only wait. If the data is important, it is recommended to save it to external storage, cleaning the system.
Enigma

The Enigma ransomware virus began infecting the computers of Russian users at the end of April 2016. The AES-RSA encryption model is used, which is found in most ransomware viruses today. The virus penetrates the computer using a script that the user runs by opening files from a suspicious email. Still no universal remedy to combat the Enigma ransomware. Users with an antivirus license can ask for help on the developer's official website. A small “loophole” was also found - Windows UAC. If the user clicks “No” in the window that appears during the virus infection process, he will be able to subsequently restore information using shadow copies.
Granit

A new ransomware virus, Granit, appeared on the Internet in the fall of 2016. Infection occurs according to the following scenario: the user launches the installer, which infects and encrypts all data on the PC, as well as connected drives. Fighting the virus is difficult. To remove you can use special utilities from Kaspersky, but the code has not yet been decrypted. Perhaps restoring previous versions of the data will help. In addition, a specialist who has extensive experience can decrypt, but the service is expensive.
Tyson

Was spotted recently. It is an extension of the already known ransomware no_more_ransom, which you can learn about on our website. Gets to personal computers from Email. Many corporate PCs were attacked. The virus creates Text Document with instructions for unlocking, offering to pay a “ransom”. The Tyson ransomware appeared recently, so there is no unlocking key yet. The only way to restore information is to return previous versions if they were not deleted by a virus. You can, of course, take a risk by transferring money to the account specified by the attackers, but there is no guarantee that you will receive the password.
Spora

At the beginning of 2017, a number of users became victims of the new Spora ransomware. In terms of its operating principle, it is not very different from its counterparts, but it boasts a more professional design: the instructions for obtaining a password are better written, and the website looks more beautiful. The Spora ransomware virus was created in C language and uses a combination of RSA and AES to encrypt the victim’s data. As a rule, computers on which the 1C accounting program was actively used were attacked. Virus hiding in disguise simple account in .pdf format, forces company employees to launch it. No treatment has been found yet.
1C.Drop.1

This 1C encryption virus appeared in the summer of 2016, disrupting the work of many accounting departments. It was developed specifically for computers that use 1C software. Once on the PC via a file in an email, it prompts the owner to update the program. Whatever button the user presses, the virus will begin encrypting files. Dr.Web specialists are working on decryption tools, but no solution has been found yet. This is due to the complex code, which may have several modifications. The only protection against 1C.Drop.1 is user vigilance and regular archiving of important documents.
da_vinci_code

New ransomware with unusual name. The virus appeared in the spring of 2016. It differs from its predecessors in its improved code and strong encryption mode. da_vinci_code infects the computer thanks to an executive application (usually attached to email), which the user launches independently. The da Vinci coder copies the body into system directory and registry, providing automatic start at turning on Windows. Each victim's computer is assigned a unique ID (helps to obtain a password). It is almost impossible to decrypt the data. You can pay money to attackers, but no one guarantees that you will receive the password.
[email protected] / [email protected]
Two email addresses that were often accompanied by ransomware viruses in 2016. They serve to connect the victim with the attacker. Attached were the addresses of the most different types viruses: da_vinci_code, no_more_ransom and so on. It is highly recommended not to contact or transfer money to scammers. Users in most cases are left without passwords. Thus, showing that the attackers' ransomware works, generating income.
Breaking Bad

It appeared at the beginning of 2015, but actively spread only a year later. The infection principle is identical to other ransomware: installing a file from an email, encrypting data. Conventional antivirus programs, as a rule, do not notice the Breaking Bad virus. Some code cannot bypass Windows UAC, leaving the user with the option to restore previous versions of documents. No company developing anti-virus software has yet presented a decryptor.
XTBL

A very common ransomware that has caused trouble for many users. Once on the PC, the virus changes the file extension to .xtbl in a matter of minutes. A document is created in which the attacker extorts cash. Some varieties XTBL virus cannot destroy files to restore the system, which allows you to return important documents. The virus itself can be removed by many programs, but decrypting documents is very difficult. If he is the owner licensed antivirus, use technical support by attaching samples of infected data.
Kukaracha

The Cucaracha ransomware was discovered in December 2016. Virus with interesting name hides user files using the RSA-2048 algorithm, which is highly durable. Kaspersky Antivirus labeled it as Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Scatter.lb. Kukaracha can be removed from the computer so that other documents are not infected. However, infected ones are currently almost impossible to decrypt (a very powerful algorithm).
How does a ransomware virus work?

There are a huge number of ransomware, but they all work on a similar principle.
- Hitting on Personal Computer. Typically, thanks to an attached file to an email. The installation is initiated by the user himself by opening the document.
- File infection. Almost all types of files are encrypted (depending on the virus). A text document is created that contains contacts for communicating with the attackers.
- All. The user cannot access any document.
Control agents from popular laboratories
The widespread use of ransomware, which is recognized as the most dangerous threat to user data, has become an impetus for many antivirus laboratories. Every popular company provides its users with programs that help them fight ransomware. In addition, many of them help with document decryption and system protection.
Kaspersky and ransomware viruses

One of the most famous anti-virus laboratories in Russia and the world offers today the most effective tools for combating ransomware viruses. The first obstacle for a ransomware virus will be Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 s latest updates. The antivirus simply will not allow the threat to enter your computer (although it may not stop new versions). To decrypt information, the developer presents several free utilities: XoristDecryptor, RakhniDecryptor and Ransomware Decryptor. They help find the virus and select the password.
Dr. Web and ransomware

This lab recommends using their antivirus program, main feature which became file backup. The storage with copies of documents is also protected from unauthorized access by intruders. Owners licensed product Dr. Web help function is available in technical support. True, even experienced specialists cannot always resist this type of threat.
ESET Nod 32 and ransomware

This company did not stand aside either, providing its users with good protection against viruses entering their computer. In addition, the laboratory recently released free utility with current databases - Eset Crysis Decryptor. The developers say that it will help in the fight against even the newest ransomware.
Ransomware viruses have been around for a long time famous type threats. They appeared at about the same time as SMS banners, and are firmly entrenched with the latter in the top ranking of ransomware viruses.
The monetization model of the ransomware virus is simple: it blocks part of the information or the user’s entire computer, and in order to regain access to the data, it requires sending SMS, electronic money or topping up the balance. mobile number via terminal.
In the case of a virus that encrypts files, everything is obvious - to decrypt the files you need to pay a certain amount. Moreover, over the past few years, these viruses have changed the approach to their victims. If previously they were distributed according to classical schemes through warez, porn sites, substitution of search results and mass spam mailings, while infecting the computers of ordinary users, now letters are sent directly, manually, with mailboxes on “normal” domains - mail.ru, gmail, etc. And they are trying to infect legal entities, where databases and contracts fall under the ciphers.
Those. attacks have grown from quantity to quality. At one of the companies, the author happened to encounter a hardened cryptographer who arrived in the mail with a resume. The infection occurred immediately after the file was opened by personnel officers; the company was just looking for personnel and the file did not arouse any suspicion. It was a docx with AdobeReader.exe attached to it :)
The most interesting thing is that none of the heuristic and proactive sensors of Kaspersky Anti-Virus worked. Another day or 2 after infection, the virus was not detected by dr.web and nod32
So what to do with such threats? Is antivirus really useless?
The days of signature-only antiviruses are coming to an end..

G Data Total Protection 2015 — best protection from ransomware
with built-in backup module. Click and buy.
For all those affected by the actions ransomware - promotional code with a discount on the purchase of G DATA - GDTP2015. Simply enter this promo code at checkout.
Ransomware viruses have once again proven the failure of antivirus programs. SMS banners, at one time, were freely “merged” to users in temp folder and simply launched onto the entire desktop and intercepted the pressing of all service combinations from the keyboard.
The antivirus program worked wonderfully at this time :) Kaspersky, as in normal mode, displayed its inscription “Protected by Kaspersky LAB”.
Banner is not a clever malware like rootkits, but simple program, which modifies 2 keys in the registry and intercepts keyboard input.
Viruses that encrypt files have reached a new level of fraud. It's again regular program, which is not embedded in the code operating system, does not replace system files, does not read areas random access memory other programs.
It simply runs for a short time, generates an open and private key and, encrypts the files and sends the private key to the attacker. A bunch of encrypted data and a file with the hackers’ contacts are left on the victim’s computer for further payment.
It’s reasonable to think: “ Why then do you need an antivirus if it can only find malicious programs known to it?
Indeed, an antivirus program is necessary - it will protect against all known threats. However, many new species malicious code she's too tough. To protect yourself from ransomware viruses, you need to take measures; an antivirus alone is not enough. And I’ll say right away: “If your files are already encrypted, you’re in trouble. It’s not going to be easy to get them back.”

:
Don't forget about antivirus
Backing up important information systems and data, each service has its own dedicated server.
Back up important data.
:
What to do with the virus itself?
Independent actions with encrypted files
Experience communicating with antivirus technical support, what to expect?
Contacting the police
Take care of precautions in the future (see previous section).
If all else fails, maybe it's worth paying?
If you have not yet become a victim of a ransomware virus:
*Have anti-virus software on your computer with the latest updates.
Let's face it: “Antiviruses suck at dealing with new types of encryptors, but they do an excellent job against known threats" So having an antivirus on your workstation is necessary. If there are already victims, you will at least avoid the epidemic. Which antivirus to choose is up to you.
From experience, Kaspersky “eats” more memory and processor time, and for laptops hard drives with 5200 rpm it’s a disaster (often with sector reading delays of 500 ms..) Nod32 is fast, but doesn’t catch much. You can buy GDATA antivirus - the best option.
*Backup of important information systems and data. Each service has its own server.
Therefore, it is very important to remove all services (1C, taxpayer, specific automated workstations) and any software on which the life of the company depends, to separate server, even better - terminal. Better yet, place each service on its own server (physical or virtual - decide for yourself).
Do not store the 1C database in public on the network. Many people do this, but it is wrong.
If work with 1c is organized over a network with shared access for reading/writing for all employees - move 1c to the terminal server, let users work with it via RDP.
If there are few users and there is not enough money for a server OS, you can use regular Windows XP (subject to lifting restrictions on the number of simultaneous connections, i.e. needs to be patched). Although, with the same success you can install an unlicensed windows version server. Fortunately, Microsoft allows you to use it, and buy and activate it later :)
The work of users with 1c via RDP, on the one hand, will reduce the load on the network and speed up the work of 1c, on the other hand, it will prevent infection of databases.
Storing database files on a network with shared access is unsafe, but if there are no other prospects, take care of backup (see next section.)
*Backup important data.
If you haven’t made backups yet, you’re a fool, forgive me. Or say hello to your system administrator. Backups save you not only from viruses, but also from careless employees, hackers, and ultimately damaged hard drives.
You can read how and what to backup in a separate article about . The GDATA antivirus, for example, has a backup module in two versions - total protection and endpoint security for organizations ( you can buy GDATA total protection).
If you find encrypted files on your computer:
*What to do with the virus itself?
Turn off your computer and contact computer services + support for your antivirus. If you are lucky, the virus body has not yet been deleted and can be used to decrypt files. If you are unlucky (as is often the case), the virus, after encrypting the data, sends the private key to the attackers and deletes all traces of itself. This is done so that it is not possible to determine how and by what algorithm they are encrypted.
If you still have a letter with an infected file, do not delete it. Send to antivirus laboratory popular products. And don't open it again.
*Independent actions with encrypted files
What you can do:
Contact antivirus support, get instructions and, possibly, a decryptor for your virus.
Write a statement to the police.
Search the Internet for the experiences of other users who have already encountered this problem.
Take measures to decrypt files, having first copied them to a separate folder.
If you have Windows 7 or 8, you can restore previous versions of files (right-click on the folder with files). Again, don't forget to copy them first.
What not to do:
Reinstall Windows
Delete encrypted files, rename them and change the extension. The file name is very important when decrypting in the future
*Experience in communicating with antivirus technical support, what to expect?
When one of our clients caught a crypto virus.hardended, which antivirus databases not yet, requests were sent to dr.web and Kaspersky.
We liked the technical support at dr.web, Feedback appeared immediately and even gave advice. Moreover, after several days they honestly said that they couldn’t do anything and dropped it detailed instructions on how to send a request through the competent authorities.
In Kaspersky, on the contrary, the bot answered first, then the bot reported that installing an antivirus with latest databases(let me remind you, the problem is hundreds of encrypted files). A week later, the status of my request changed to “sent to the antivirus laboratory,” and when the author modestly inquired about the fate of the request a couple of days later, Kaspersky representatives replied that we would not receive a response from the laboratory yet, they say, we were waiting.
After some time, I received a message that my request was closed with an offer to evaluate the quality of the service (all this while still waiting for a response from the laboratory).. “Fuck you!” - thought the author.
NOD32, by the way, started catching this virus on the 3rd day after its appearance.
The principle is this: you are on your own with your encrypted files. Laboratories of large antivirus brands will help you only if whether you have a key for the corresponding antivirus product and if in crypto virus has a vulnerability. If attackers encrypted a file using several algorithms at once and more than once, you will most likely have to pay.
The choice of antivirus is yours, do not neglect it.
*Contact the police
If you have become a victim of a crypto virus and have suffered any damage, even in the form of encrypted personal information, you can contact the police. Instructions for application, etc. There is .
*If all else fails, might it be worth paying?
Given the relative inaction of antiviruses in relation to ransomware, it is sometimes easier to pay attackers. For hardended files, for example, the authors of the virus ask for around 10 thousand rubles.
For other threats (gpcode, etc.) the price tag can range from 2 thousand rubles. Most often, this amount turns out to be lower than the losses that the absence of data can cause and lower than the amount that craftsmen may ask you for manually decrypting files.
To summarize, the best protection against ransomware viruses is backing up important data from servers and user workstations.
It's up to you to decide what to do. Good luck.
Users who read this post usually read:
In contact with
